SERVICES AND EQUIPMENTS
We develop innovative material solutions for your sector with a highly specialized team and a wide range of cutting-edge equipment.
A WORLD OF SERVICES
At DIOPMA, we offer a wide range of specialized services in Materials Science. From technical advice and consultancy to mechanical testing and nanoscale structural characterization. Our commitment is to drive innovation through technology transfer, specialized training, and collaboration in R&D projects. We are supported by the Scientific and Technical Services of the University of Barcelona to ensure cutting-edge solutions.
WHAT CAN WE OFFER YOU?
Discover all the services we have available to meet your needs.

Specialized training for public and private sector

Technical advice and consulting.

Participation and advice in research projects

Participation and consultant in Competitive Projects

Specialized training for public and private sector

Technology transfer

Fundamental, applied research, development and innovation

Bibliographic studies on patents and regulations

Bibliometric research for research areas under development

Design and characterization of metallic, ceramic, polymeric and composite materials

Search, select and/or design of new materials

Structural, physical and chemical characterization.
CHARACTERIZATION EQUIPMENT
At DIOPMA, we offer a wide range of advanced material characterization techniques with state-of-the-art equipment
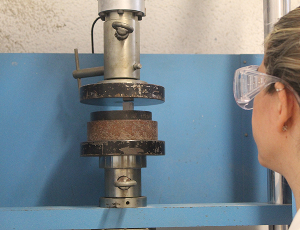
Mechanical characterization: Tensile and compression tests, bending tests, hardness tests (macro, micro and nanometric scale)

Heat treatment in resistance and induction furnaces

Durability test due to high temperature effect and thermal cycles

Thermobalance by gravimetric analysis (TGA) and simultaneus SDT

Calorimetry analysis by Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC)

Thermal conductivity by transient line heat source method and hot disk

Determination of chemical oxygen demand (COD)

Humidity determination

Determination of pH

Flocculator

Thermostatic bath

UV-VIS spectrophotometer

Determination of Oxygen Index (LOI) according to ASTM D 2863 (1970) or ISO 4589 (1984)

Nanoindenter with continuous stiffness measurement module (Noano Indenter XP with CSM).

Rheology analysis

FT-IR composition analysis

Chemical composition by X-ray fluorescense. (XRF)

Silicon printing 3D

Tam Air

OTHER TECHNIQUES AVAILABLES
The DIOPMA Center utilizes the infrastructure of the Scientific and Technical Services of the University of Barcelona (CCiTUB). Click here to view the complete list of these services
CONTACT DIOPMA
Tell us how we can help you and our team will contact you.

© 2025 Centre Diopma. All rights reserved. Legal notice